- Welcome To Reid Health
-
How Can We Help You
All Services
- Allergy Care
- Athletic Training Clinic
- Breast Center
- Cancer Center
- Dental Health
- Dermatology
- Diabetes & Nutrition Education
- Ear, Nose, & Throat
- Emergency Care
- Endocrinology
- Family Birthing Center
- Gastroenterology
- General Surgery
- Hearing Care
- Heart & Vascular Center
- Home Health
- Home Medical Equipment
- Hospice Services
- Hospitalist Service
- Infectious Disease
- Joint and Spine Center
- Laboratory Services
- Neurology
- OB/GYN
- One Call Access
- Orthopedics/Spine
- PACE
- Pain Management
- Palliative Care
- Pediatrics
- Perioperative Clinic
- Pharmacy
- Plastic & Reconstructive
- Podiatry
- Primary Care
- Psychiatrics
- Pulmonology
- Radiation Therapy
- Radiology
- Ready Care Clinic
- Rehabilitation
- Reid Fitness
- Revive Spa & Skincare
- Robotics & Technology
- Sleep Center
- Sports Medicine
- Telehealth
- Urgent Care
- Urogynecology
- Urological Care
- Vein Center
- Wound Healing Center
-
Find Your Provider
-
Find Your Nearest Location
How Can We Care for You Today?
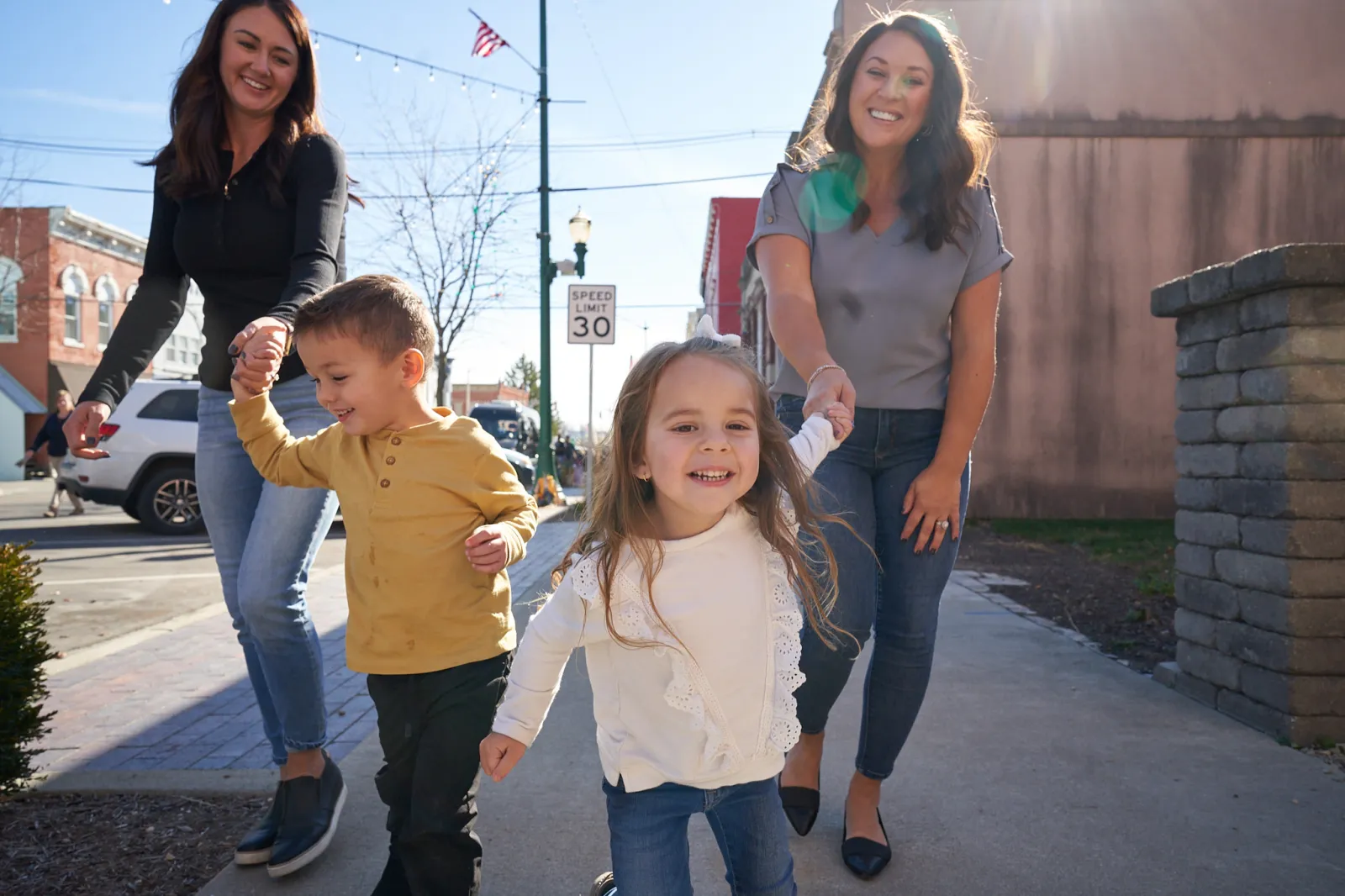

Reid Health's mission is to lead our communities to well-being, one person at a time. Whether you're seeking urgent care, need to schedule a new patient appointment, or want to connect with your existing care team, we're here to help.
- Urgent Care- Quickly view wait times and save an appointment spot with On My Way
- New Patient Appointment - No provider? No problem. Choose from a list of providers offering open-scheduling and select an appointment time slot that works for you.
- Schedule with Your Current Care Team - Established Reid Health patient who needs a new appointment? Schedule a visit or pre-register for labs by self-scheduling. You'll be directed to log in to MyChart to view your scheduling options.
If you have questions about connecting to care, we can help! Select request an appointment and we'd be happy to assist.
Find a Location Near you
We want to show Who We Are!
Reid Health offers nationally recognized quality and technology with a personal touch that sets us apart. Our growing team is known for going the extra mile to make sure our patients and families are made to feel as comfortable and cherished as possible when they find themselves in need of our services - on the main campus or at one of numerous satellite facilities in the region of Indiana and Ohio that we serve.







Get Connected
Wellness Blog
-
Ensure eye safety for total eclipse viewing with special-purpose safe solar filters
-
Health changes you should share with your primary care provider
-
Diagnosing and treating cervical spinal stenosis
More Wellness PostsPress Releases
-
Kaleidoscope raises nearly $100,000 for cancer care and prevention
-
Get in free at Preble County Chamber of Commerce Expo thanks to Reid Health
-
April Ambassador ‘has a heart of gold’
More Press ReleasesPodcasts
-
Primary Care
-
Pediatric Care
-
Mako Robotic Joint Replacements
More PodcastsUpcoming Events
-
Reid Health Blood Drive | Connersville Apr 23, 2024 at 10 a.m.
-
Stroke Support Group Apr 23, 2024 at 1 p.m.
-
Revive Spa: Spring Cleaning Event Apr 29, 2024 at 4:30 p.m.
More Upcoming Events